Parse Config Arguments 会从命令行参数中获取有关 Model, Runtime, Parallel Processing & Input 有关的信息。前三者被包含在 engine_config 中,而最后者则被包含在 input_config 中。在 create_config() 函数中,会初始化 _WORLD 全局变量,它是一个 GroupCoordinator 实例。很明显它只有一个包含所有的设备进程组。
GroupCoordinator 类是一个 PyTorch 的进程组封装器,主要用于管理一组进程之间的通信。它可以根据不同的通信后端(如 NCCL、Gloo、MPI 等)来协调进程之间的操作。包含以下信息
rank: 当前进程的全局索引(全局唯一)。ranks: 组内所有进程的全局索引列表。world_size: 组的大小,即进程的数量 len(ranks)local_rank: 当前进程在本地节点中的索引。rank_in_group: 当前进程在组内的索引。cpu_group: 用于 CPU 通信的进程组。device_group: 用于设备(如 GPU)通信的进程组。1 2 3 4 5 6 if we have a group of size 4 across two nodes:in Group0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3
__init__ 方法接收以下参数:
group_ranks: 一个包含多个进程索引列表的列表,每个子列表表示一个进程组。local_rank: 当前进程的本地索引。torch_distributed_backend: 指定用于通信的后端类型 (如 “gloo” 或 “nccl”).初始化过程:
使用 torch.distributed.get_rank() 获取当前进程的全局索引。 遍历传入的 group_ranks 列表,为每个子列表创建一个新的设备组和 CPU 组。 如果当前进程的索引在当前子列表中,则设置该进程的组内信息 (包括 ranks、world_size 和 rank_in_group). 确保 CPU 组和设备组都已成功创建。 根据是否可用 CUDA 设置当前设备为 GPU 或 CPU.
1 2 3 4 5 6 def main ():"xFuser Arguments" )
关于可以支持的并行策略如下,包括 Data Parallel, Sequence Parallel, Pipefusion Parallel & Tensor Parallel.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Parallel Processing Options:split batch in classifier_free_guidance. cfg_degree will be 2 if set in attention layer.in attention layer.in pipefusion parallel.in pipefusion parallelfor tensor parallel.
从 CLI 解析的参数后会在 create_config() 中组成如下的 ParallelConfig .
DataParallelConfig: 总的并行度为 dp_degree * cfg_degree.
dp_degree: 相当于对 batch 维度进行切分,cfg_degree: Class-free Guidance(cfg) 用于控制无条件的图片生成 (若使用相当于 batchsize *= 2).
SequenceParallelConfig: 总的并行度为 sp_degree = ulysses_degree * ring_degree
ulysses_degree: 用于控制 DeepSeed-Ulesses 的序列并行度。ring_degree: 用于控制计算 Ring Attention 时对 Q K V 沿着 Sequence 维度的切分块数。
TensorParallelConfig: 总的并行度为 tp_degree.
PipeFusionParallelConfig: 总的并行度为 pp_degree=num_pipeline_patch.
pp_degree: 用于控制 PipeFusion 中模型 Transoformer Blocks 的切分个数。num_pipeline_patch: 用于控制对 latent feature map 的切分块数.attn_layer_num_for_pp: 是一个 list,表示 pp_degree 里每个 stage 的 Transformer 层数。
关于 PipeFusion,原文说切分的 patch 数和 pipeline 大小可以不同,但这里要求 len(attn_layer_num_for_pp)=pp_degree
设备数必须等于 dp_degree * cfg_degree * sp_degree * tp_degree * num_pipeline_patch,并且 pp_degree 必须小于等于设备数。ulysses_degree 必须要大于且能被 attention 的头数整除。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 parallel_config = ParallelConfig(self .data_parallel_degree,self .use_cfg_parallel,self .ulysses_degree,self .ring_degree,self .tensor_parallel_degree,self .split_scheme,self .pipefusion_parallel_degree,self .num_pipeline_patch,self .attn_layer_num_for_pp,
Construct Pipeline 解析完配置参数并构建了 engine_config 后,下一步是构建模型的 pipeline.
1 2 3 4 5 6 pipe = xFuserPixArtAlphaPipeline.from_pretrained( f"cuda:{local_rank} " )
xFuserPixArtAlphaPipeline 继承自 xFuserPipelineBaseWrapper ,_init_runtime_state 函数经过一番调用后会使用 initialize_model_parallel 初始化 _RUNTIME 有关模型参数的部分和模型并行的全局变量 _DP, _CFG, _PP, _SP, _TP,它是一个 DiTRuntimeState (继承 RuntimeState) 实例,记录了每个 Group 包含的设备索引,除此之外还包括 PipeFusionParallel 中有关 patch 索引的参数 (在稍后 pipeline 执行的时候计算).
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 class xFuserPipelineBaseWrapper (xFuserBaseWrapper, metaclass=ABCMeta):def __init__ ( self, pipeline: DiffusionPipeline, engine_config: EngineConfig, ):self .module: DiffusionPipelineself ._init_runtime_state(pipeline=pipeline, engine_config=engine_config)getattr (pipeline, "transformer" , None )getattr (pipeline, "unet" , None )getattr (pipeline, "vae" , None )getattr (pipeline, "scheduler" , None )if transformer is not None :self ._convert_transformer_backbone(transformer)elif unet is not None :self ._convert_unet_backbone(unet)if scheduler is not None :self ._convert_scheduler(scheduler)super ().__init__(module=pipeline)def _convert_transformer_backbone ( self, transformer: nn.Module, ):"Transformer backbone found, paralleling transformer..." )return transformer
initialize_model_parallel 该函数中会初始化一个 RankGenerator,它接收每个并行方法的设备组大小和并行度大小顺序。其主要的方法是通过 generate_masked_orthogonal_rank_groups 函数确定每个并行组由包含哪些设备,先把并行方法按照并行度从小到大排列成 tp-sp-pp-cfg-dp. 再根据要生成的并行组产生对应的 mask. 即如果要生成 pp 组对应的 rank,那么 mask = [0, 0, 1, 0, 0]
该函数首先会生成需要生成的并行组的大小组成的 masked_shape 和不需要生成的 unmasked_shape. 首先要用 prefix_product 计算 global_stride,即每个并行度的设备组包含几个设备。再根据 mask 取出对应的 mask_stride 和 unmaskd_stride. group_size = mask_stride[-1] 即为最大并行度的组包含的设备数。num_of_group = num_of_device / mask_stride[-1] 即为要生成几个并行度最大的组。先遍历要生成的每个设备组,并用 decompose 函数确定该设备组在不需要并行维度上的索引;再遍历该组中的每个设备的 lock rank,确定该设备在需要并行维度上的索引,最后用 inner_product 确定该设备的 global rank.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 def generate_masked_orthogonal_rank_groups ( world_size: int , parallel_size: List [int ], mask: List [bool ] List [List [int ]]:def prefix_product (a: List [int ], init=1 ) -> List [int ]: for v in a:return rdef inner_product (a: List [int ], b: List [int ] ) -> int :return sum ([x * y for x, y in zip (a, b)])def decompose (index, shape, stride=None ): """ This function solve the math problem below: There is an equation: index = sum(idx[i] * stride[i]) And given the value of index, stride. Return the idx. This function will used to get the pp/dp/pp_rank from group_index and rank_in_group. """ if stride is None :for s, d in zip (shape, stride)] assert (sum ([x * y for x, y in zip (idx, stride[:-1 ])]) == index"idx {} with shape {} mismatch the return idx {}" .format (index, shape, idx)return idxfor s, m in zip (parallel_size, mask) if m] for s, m in zip (parallel_size, mask) if not m] for d, m in zip (global_stride, mask) if m]for d, m in zip (global_stride, mask) if not m]1 ] for group_index in range (num_of_group): for rank_in_group in range (group_size): return ranks
Hybrid Parallelsim Design xDiT支持四种并行方式:PipeFusion、Sequence、Data 和 CFG Parallel。其中,Data 和 CFG Parallel在图像间并行相对简单,而 PipeFusion和 Sequence 在图像内部的不同 Patch 间并行则较为复杂。能
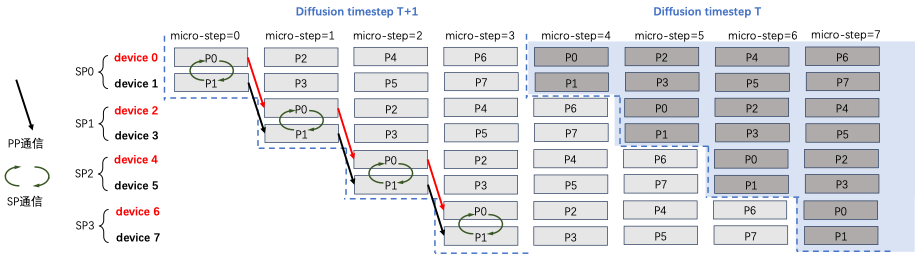
PipeFusion 利用 Input Tempor Redundancy特点,使用过时的 KV(Stale KV)进行 Attention 计算,这使得 PipeFusion 无法像大型语言模型那样轻松地实现并行策略的混合。使用标准的序列并行接口,如RingAttention、Ulysses或 USP,无法满足 SP 与PipeFusion混合并行的需求。
我们对这个问题具体说明,下图展示了pipe_degree=4,sp_degree=2的混合并行方法。设置 num_pipeline_patch=4,图片切分为 M=num_pipeline_patch*sp_degree=8 个 Patch,分别是 P0~P7.
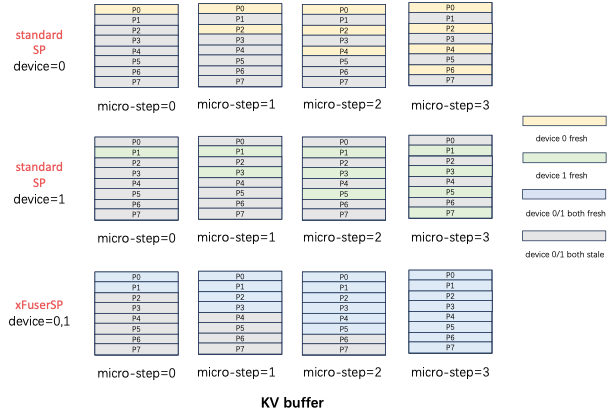
Standard SP Attention 的输入Q,K,V 和输出 O 都是沿着序列维度切分,且切分方式一致。如果不同 rank 的输入 patch 没有重叠,每个 micro step 计算出 fresh KV 更新的位置在不同 rank 间也没有重叠。如下图所示,standard SP 的 KV Buffer 中黄色部分是 SP0 rank=0 拥有的 fresh KV,绿色部分是 SP1 rank=1 拥有的fresh KV,二者并不相同。在这个 diffusion step 内,device=0 无法拿到 P1,3,5,7 的 fresh KV 进行计算,但是 PipeFusion 则需要在下一个 diffusion step 中,拥有上一个diffusion step 全部的 KV. standard SP 只拥有 1/sp_degree 的 fresh kv buffer,因此无法获得混合并行推理正确的结果。
xDiT专门定制了序列并行的实现方式,以适应这种混合并行的需求。xDiT使用 xFuserLongContextAttention 把SP的中间结果存在 KV Buffer 内。效果如下图,每个 micro-step SP 执行完毕后,SP Group 内不同 rank 设备的 fresh KV是 replicate 的。这样一个 diffusion step 后,SP Group 所有设备的 KV Buffer 都更新成最新,供下一个 Diffusion Step 使用。
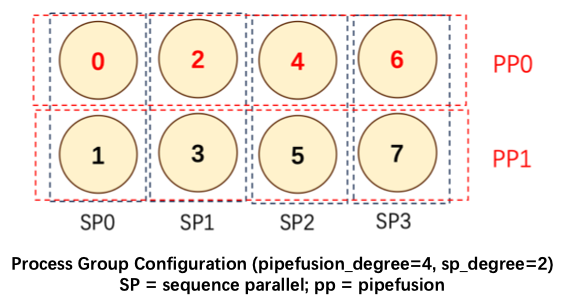
假设一共有 16 个 GPU,索引表示为 g0 … g15,并行方法和并行度设置如下
dp_degree (2) * cfg_degree (2) * pp_degree (2) * sp_degree (2) = 16.
那么一共会创建 2 data parallel-groups, 8 CFG groups, 8 pipeline-parallel groups & 8 sequence-parallel groups:
2 data-parallel groups: 8 CFG-parallel groups: 8 pipeline-parallel groups: 8 sequence-parallel groups:
Convert Model _split_transformer_blocks 会对 transformer block 进行分配,如果 parallel_config 指定了 attn_layer_num_for_pp,即存有每个 pipeFusion 的设备被分配的 transformer block 数量的列表,按其进行分配;否则平均分。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 def _split_transformer_blocks (self, transformer: nn.Module, ):if attn_layer_num_for_pp is not None :if is_pipeline_first_stage():0 ]]else :sum (attn_layer_num_for_pp[: pp_rank - 1 ]) : sum (attn_layer_num_for_pp[:pp_rank])]else : len (transformer.transformer_blocks) + pp_world_size - 1 ) // pp_world_sizemin ((pp_rank + 1 ) * num_blocks_per_stage, len (transformer.transformer_blocks),)if not is_pipeline_first_stage():None if not is_pipeline_last_stage():None None return transformer
同时也会 convert 原先的 transformer backbone 为 xFuserPixArtTransformer2DWrapper ,具体表现为只有 pipeline 的第一阶段进行 position embedding,最后一阶段进行 unpatchify 变为原来的图像形状。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 @xFuserTransformerWrappersRegister.register(PixArtTransformer2DModel ) class xFuserPixArtTransformer2DWrapper (xFuserTransformerBaseWrapper ):def __init__ ( self, transformer: PixArtTransformer2DModel, ):super ().__init__("attn1" ], @xFuserBaseWrapper.forward_check_condition def forward ( self, hidden_states: torch.Tensor, encoder_hidden_states: Optional [torch.Tensor] = None , timestep: Optional [torch.LongTensor] = None , added_cond_kwargs: Dict [str , torch.Tensor] = None , cross_attention_kwargs: Dict [str , Any ] = None , attention_mask: Optional [torch.Tensor] = None , encoder_attention_mask: Optional [torch.Tensor] = None , return_dict: bool = True , ): ''' ...... ''' self ._get_patch_height_width()if is_pipeline_first_stage():self .pos_embed(hidden_states)''' ...... ''' if is_pipeline_last_stage():''' ...... ''' else :if not return_dict:return (output,)return Transformer2DModelOutput(sample=output)
Pipeline Execution 在进行 warm up 后便会进行模型推理和采样器的去噪过程。模型推理通过调用 pipeline 的 __call__ 方法实现。在原先 diffusers 包中的 PixaeArtAlphaPipeline 基础上做了一些修改。我们直接看修改的部分。
get_runtime_state() 返回 _RUNTIME ,再调用 set_input_parameters 方法,设置输入参数和计算 PipeFusionParallel 中有关 patch 索引的参数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 get_runtime_state().set_input_parameters(
该函数会计算
pipeline parallel 中每个 patch 的高度,必须是 patch_size * num_sp_patches 的整数倍。
将每个流水线阶段的 patch 高度均匀地分配给 num_sp_patches 个序列并行设备,计算每个设备的 patch 高度和起始索引。
然后会对 prompt 嵌入后的正样本和负样本在 cfg parallel 组中的设备进行分割, rank 0 负样本,rank 1 正样本。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 if do_classifier_free_guidance:self ._process_cfg_split_batch(negative_prompt_embeds,def _process_cfg_split_batch (self, concat_group_0_negative: torch.Tensor, concat_group_0: torch.Tensor, concat_group_1_negative: torch.Tensor, concat_group_1: torch.Tensor, ):if get_classifier_free_guidance_world_size() == 1 :0 )0 )elif get_classifier_free_guidance_rank() == 0 :elif get_classifier_free_guidance_rank() == 1 :else :raise ValueError("Invalid classifier free guidance rank" )return concat_group_0, concat_group_1
Async Pipeline Initialize Pipeline 首先会初始化 pipeline,rank 0 会接收 warmup 阶段的 latents 然后沿着 H 维度进行分块,rank -1 也会沿着 H 维度进行分块。然后为每个 patch 创建接收的任务,注意 rank 0 第一次是从 warmup 阶段接收 latents,所以他的需要接收的 timestep 少一个。patch_latents 表示当前设备正在处理的 patch 数据,它会在流水线的每一阶段进行处理和传递。last_patch_latents 只在流水线的最后阶段设备中使用,用来存储每个 patch 的最终计算结果。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 if len (timesteps) == 0 :return latentsself ._init_async_pipeline(len (timesteps),None for _ in range (num_pipeline_patch)]if (is_pipeline_last_stage())else None def _init_async_pipeline ( self, num_timesteps: int , latents: torch.Tensor, num_pipeline_warmup_steps: int , True )if is_pipeline_first_stage():if num_pipeline_warmup_steps > 0 else latents)list (latents.split(get_runtime_state().pp_patches_height, dim=2 ))elif is_pipeline_last_stage():list (latents.split(get_runtime_state().pp_patches_height, dim=2 ))else :None for _ in range (get_runtime_state().num_pipeline_patch)]1 if is_pipeline_first_stage() else num_timesteps)for _ in range (recv_timesteps):for patch_idx in range (get_runtime_state().num_pipeline_patch):return patch_latents
Iterate Over Timesteps 对于每个 timestep(即每个去噪步骤),会对每个 patch 执行:
如果当前设备是流水线的最后一阶段 (is_pipeline_last_stage()),将当前 patch 的数据保存到 last_patch_latents 中。
如果不是第一阶段的第一个时间步 (i == 0),调用 recv_next() 来异步接收来自上一设备的 patch 数据(非阻塞操作,通过 irecv 完成)。
对每个 patch 执行模型的前向传播 _backbone_forward,根据当前时间步 t 进行推理和计算。
如果当前设备是最后一阶段,调用 _scheduler_step 来根据噪声进行去噪,并将数据发送给下一个设备 pipeline_isend。
对于非最后阶段的设备,继续将当前 patch 的计算结果发送到下一设备。
get_pp_group().pipeline_isend 用于将当前 patch 发送到下一个设备,使用的是 torch.distributed.isend,这是非阻塞发送。get_pp_group().recv_next 会准备好接收来自上一个设备的数据,recv_buffer 用来存放接收到的数据。irecv 实现非阻塞接收,可以在等待数据的同时进行其他操作。
scheduler_step 只对单独的 patch 进行,原因未知。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 first_async_recv = True for i, t in enumerate (timesteps):for patch_idx in range (num_pipeline_patch):if is_pipeline_last_stage():if is_pipeline_first_stage() and i == 0 :pass else :if first_async_recv:False self ._backbone_forward(if is_pipeline_last_stage():self ._scheduler_step(if i != len (timesteps) - 1 :else :if is_pipeline_first_stage() and i == 0 :pass else :if i == len (timesteps) - 1 and patch_idx == num_pipeline_patch - 1 :pass else :if i == len (timesteps) - 1 or (1 ) > num_warmup_stepsand (i + num_pipeline_warmup_steps + 1 ) % self .scheduler.order == 0 assert callback is None , "callback not supported in async " "pipeline" if (is not None and i + num_pipeline_warmup_steps % callback_steps == 0 getattr (self .scheduler, "order" , 1
Construct Final Latents timestep 遍历完成后,仍然有最后的操作要进行,这些操作的主要目的是将流水线并行中各个 patch 的结果拼接起来,形成完整的输出结果。尤其是对于最后一个设备,还需要处理 序列并行(sequence parallelism) 的合并操作。通过 all_gather 操作将每个设备上处理的 patch 结果收集起来,然后从每个设备的 sp_latents_list 中,提取出对应于 pp_patch_idx 的 patch 数据并将它们拼接起来。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 latents = None if is_pipeline_last_stage():2 )if get_sequence_parallel_world_size() > 1 :True for pp_patch_idx in range (get_runtime_state().num_pipeline_patch):1 ],for sp_patch_idx in range (sp_degree)2 )return latents
Decode Latents 为了避免 VAE 中的 Decoder 在对 8192px 分辨率图像进行 conv2D 的过程中出现 OOM 的问题, xDiT 使用了序列并行和 patch 并行的 PatchConv2d 和 PatchGroupNorm 来替换掉原有 Decoder 中的 UpDecoderBlock2D 对应的层。
PatchGroupNorm PatchGroupNorm 在 H 维度上划分为多个 patch,每个设备求自己所负责的部分和。
假设输入张量 x 的形状为 [N, C, H, W],其中 N 表示批量大小(Batch Size),C 表示通道数(Channels),H 和 W 分别表示高度和宽度。在 GN 中,通道数 C 被划分为 G 组,每个组包含 C/G 个通道。计算每个组内即 [C/G, H, W] 维度上的均值和方差。特别的 G=1 时,GN 退化为 BN。G=C 时,GN 退化为 LN。
获取高度信息
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 class PatchGroupNorm (nn.Module):''' def __init__(self, ...)''' def forward (self, x: Tensor ) -> Tensor:2 ], dtype=torch.int64, device=x.device)
计算每个组的通道数量以及每个进程内的元素数量
1 2 3 channels_per_group = x.shape[1 ] // self .num_groups 2 ] * x.shape[-1 ] 1 ]
计算每个组的均值
1 2 3 4 5 x = x.view(x.shape[0 ], self .num_groups, -1 , x.shape[-2 ], x.shape[-1 ]) 2 ,3 ,4 ), dtype=torch.float32) None , None , None ].to(x.dtype)
计算每个组的方差
1 2 3 4 5 6 0 ], self .num_groups), dtype=torch.float32, device=x.device)2 ,3 ,4 ), out=group_var_sum) None , None , None ].to(x.dtype)
归一化并缩放
1 2 3 x = (x - E) / torch.sqrt(var + self .eps)self .weight[:, :, None , None , None ] + self .bias[:, :, None , None , None ]return x
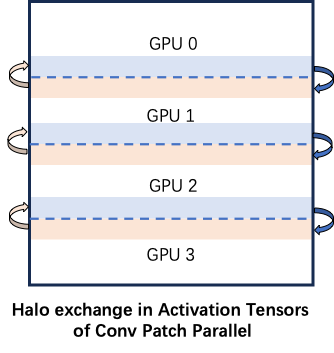
PatchConv2d PatchConv2d 将潜在空间中的特征映射分割成多个 patch,跨不同设备进行序列并行 VAE 解码。这种技术将中间激活所需的峰值内存减少到 1/N,其中 N 是所使用的设备数量。对于 VAE 中的卷积算子,需要对如下图所示的 halo 区域数据进行通信。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class PatchConv2d (nn.Conv2d):def __init__ ( self, in_channels: int , out_channels: int , kernel_size: _size_2_t, stride: _size_2_t = 1 , padding: Union [str , _size_2_t] = 0 , dilation: _size_2_t = 1 , groups: int = 1 , bias: bool = True , padding_mode: str = 'zeros' , device=None , dtype=None , block_size: Union [int , Tuple [int , int ]] = 0 ) -> None :if isinstance (dilation, int ):assert dilation == 1 , "dilation is not supported in PatchConv2d" else :for i in dilation:assert i == 1 , "dilation is not supported in PatchConv2d" self .block_size = block_sizesuper ().__init__(
_conv_forward 函数是 PatchConv2d 类的核心,它负责在输入张量上执行卷积操作,特别是在分布式计算场景下处理跨进程的输入切分、halo 区域的传递和计算。以下是使用的辅助函数的简要功能说明
_get_world_size_and_rank :获取当前分布式环境中的进程总数 world_size 和当前进程的编号 rank_calc_patch_height_index:根据每个进程的输入高度,计算所有进程的起始和结束高度索引。_calc_halo_width_in_h_dim:计算当前进程在 h 维度上所需的上方和下方的 halo 区域宽度。_calc_bottom_halo_width:计算当前进程从下方相邻进程需要接收的 halo 区域的宽度。_calc_top_halo_width:计算当前进程从上方相邻进程需要接收的 halo 区域的宽度。_adjust_padding_for_patch:根据当前进程的 rank 和总进程数调整输入数据的填充方式,防止边界重复计算。
获取输入信息以及通信组信息
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 def _conv_forward (self, input : Tensor, weight: Tensor, bias: Optional [Tensor] ):input .shapeself ._get_world_size_and_rank()if (world_size == 1 ): if self .padding_mode != 'zeros' :return F.conv2d(F.pad(input , self ._reversed_padding_repeated_twice, mode=self .padding_mode),self .stride,0 ), self .dilation, self .groups)return F.conv2d(input , weight, bias, self .stride,self .padding, self .dilation, self .groups)
获取输入的元数据
1 2 3 4 patch_height_list = [torch.zeros(1 , dtype=torch.int64, device=f"cuda:{rank} " ) for _ in range (dist.get_world_size())]f"cuda:{rank} " )) self ._calc_patch_height_index(patch_height_list) self ._calc_halo_width_in_h_dim(rank, patch_height_index, self .kernel_size[0 ], self .padding[0 ], self .stride[0 ])
计算相邻进程的 halo 区域 (也就是自己需要接发送的部分)
通过计算前一个进程的 bottom_halo_width 和后一个进程的 top_halo_width 得出自己需要发送的部分
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 prev_bottom_halo_width: int = 0 int = 0 if rank != 0 :self ._calc_bottom_halo_width(rank - 1 , patch_height_index, self .kernel_size[0 ], self .padding[0 ], self .stride[0 ])if rank != world_size - 1 :self ._calc_top_halo_width(rank + 1 , patch_height_index, self .kernel_size[0 ], self .padding[0 ], self .stride[0 ])max (0 , next_top_halo_width)
进行 halo 区域的发送与接收
异步发送,同步接收
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 to_next = None None None None if next_top_halo_width > 0 :input [:, :, -next_top_halo_width:, :].contiguous()1 )if halo_width[0 ] > 0 : 0 ], w], dtype=input .dtype, device=f"cuda:{rank} " )1 )if prev_bottom_halo_width > 0 : input [:, :, :prev_bottom_halo_width, :].contiguous()1 )if halo_width[1 ] > 0 :1 ], w], dtype=input .dtype, device=f"cuda:{rank} " )1 )
拼接 halo 区域
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 if halo_width[0 ] < 0 : input = input [:, :, -halo_width[0 ]:, :]if top_halo_recv is not None : input = torch.cat([top_halo_recv, input ], dim=-2 )if bottom_halo_recv is not None :input = torch.cat([input , bottom_halo_recv], dim=-2 )
等待发送完成再开始计算
1 2 3 4 if to_next is not None :if to_prev is not None :
进行卷积和后处理
为了减少 memory spike 一次计算 block_size*block_size 的区域,并将结果拼接起来
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 padding = self ._adjust_padding_for_patch(self ._reversed_padding_repeated_twice, rank=rank, world_size=world_size)if self .block_size == 0 or (h <= self .block_size and w <= self .block_size):if self .padding_mode != 'zeros' :input , padding, mode=self .padding_mode),self .stride, _pair(0 ), self .dilation, self .groups)else :input , weight, bias, self .stride,self .padding, self .dilation, self .groups)return conv_reselse :if self .padding_mode != "zeros" :input = F.pad(input , padding, mode=self .padding_mode)elif self .padding != 0 :input = F.pad(input , padding, mode="constant" )input .shapeself .block_size - 1 ) // self .block_size self .block_size - 1 ) // self .block_size for idx_h in range (num_chunks_in_h):for idx_w in range (num_chunks_in_w):1 ) * unit_chunk_size_w1 ) * unit_chunk_size_hinput [:, :, start_h:end_h, start_w:end_w],self .stride,0 ,self .dilation,self .groups,1 ))return torch.cat(outputs, dim=-2 )